Heart Rate Tracking with Myzone®
View All Section Pages
Numerous benefits result from regularly tracking your heart rate including identifying your true exercise intensity to achieve fitness goals or performance results.
- Accurately measure exercise intensity
When exercising, what may feel intense may not actually be “intense exercise.” It really may be fatigue, dehydration or lack of fuel. When we are not feeling our best, it is wise to exercise moderately or at a lower intensity as the body is already in a stressed state. We should not perform high-intensity exercise to add to the current distressed state. Heart rate tracking allows us to see if we are over trained or an underlying issue may exist. If your heart rate is abnormally elevated during a familiar activity, it is wise to consider why this is occurring and decrease exercise intensity or stop exercise altogether for that session and consult your physician if it recurs.
- Achieve fitness or performance results
If you are seeking results, it is important that you exercise in the right zones to achieve performance or fitness goals.
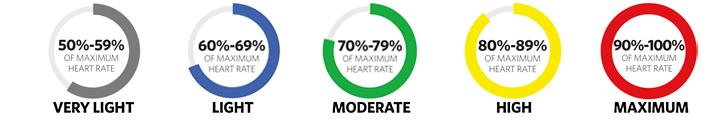
Most often, we are not exercising at an intensity sufficient enough to produce weight loss, enhance cardiovascular capacity or simply enhance our ability to recover from activity (a true sign of fitness). Using Myzone® can guide you to understand if you are exercising in the healthy zones according to what goal you are trying to achieve. Blue and green (light to moderate) zones are geared towards improving overall health and fitness. Yellow and red (high to maximum) zones, on the other hand, are helpful for performance gains or enhanced fitness results through higher intensity training periods. Recovery from these types of work phases is necessary to incorporate into the same workout session by returning to the blue zone between the high intensity training periods.
Why are the different Myzone® training zones important?
Life is not stagnant! We have the ability to move at different speeds in different durations. We may walk at a steady state for 30-45 minutes or sprint to help someone in need. Our cardiovascular system can be trained in differing intensities, too. There are benefits to exercising in ALL zones.
In 1989, Kenneth H. Cooper, MD, MPH, and researchers at The Cooper Institute were the first to prove that exercise was good for your health. The landmark study shows that being fit reduces the risk of dying of all causes by 58 percent. The Cooper Institute has shown moderate activity levels in the blue and green zones to have a myriad of health benefits including:
- Improvement of blood pressure management
- Increase healthy HDL cholesterol
- Advancement of cardiovascular functions
- Lower triglycerides
- Decrease risk for heart disease and stroke
American College of Sports Medicine has shown benefits to exercising in higher heart rate zones, or as the fitness industry fondly terms “HIIT,” or high-intensity interval training (the yellow and red zones). HIIT is incorporating periods of higher intensity work (> 80% maximum heart rate (ACSM)) within an exercise session. This may be accomplished by increasing resistance (for example, increasing resistance on the elliptical or bike) or increasing movement speed (for example, walking faster, sprinting or moving faster on an elliptical, etc.) for a set period of time. It should feel “hard!” After this hard period of work, it is recommended to recover 40-60% maximum heart rate (light gray to blue zones). You then alternate these work periods over the course of an exercise session.
The benefits of HIIT are shown to be:
- Improvement of aerobic and anaerobic fitness (“increase cardiovascular capacity”)
- Decrease in blood pressure
- Increase in insulin sensitivity
- Enhance cholesterol profiles
- Shred abdominal fat and body weight while maintaining muscle
If you have been cleared to exercise, you can explore HIIT. It can and should look different for every person depending on their goals and existing fitness levels. Many research studies use a 1:1 work to recovery ratio when performing HIIT. Benefits have also been proven in using shorter, higher intensity work periods followed by longer (greater than the work interval length) periods of recovery.
Try incorporating one of these easy HIIT examples in your next workout:
- 30 seconds “sprint” or very hard effort /90 seconds-4 minutes active recovery. Repeat for approximately 10-20 minutes.
- 1 minute hard effort /1 minute active recovery. Repeat for 10-20 minutes.
- 3 minutes moderately hard effort /2-4 minutes active recovery. Repeat for 15-30 minutes.
- “Interval” programs on cardio equipment
How does Myzone® calculate my max heart rate and thus, training zones?
The equation Myzone® uses is based off of the HUNT Fitness study, which showed to be more accurate than 220-age. Myzone’s backend equation for estimating maximum heart rate is 211 – (0.64 x age in years). This equation has been found to be most accurate for Myzone® users and better suited for exercisers of all ages, especially active aging adults.
Heart rate tracking is important and beneficial for all fitness levels and forms of exercise. There are a wide variety of effective heart rate trackers on the market today that come in chest straps or watch form including Polar, Fitbit, Garmin or Wahoo. Because various factors play into how your body perceives the frequency, duration and intensity of your workouts, it is helpful to physically track your workouts with a heart rate tracking device. By providing objective measurements of how hard your body is working, heart rate tracking can greatly help you meet even your highest of fitness goals by improving the way you go about exercising.
For more information about Cooper Fitness Center or to schedule a session with a Professional Fitness Trainer, visit cooperfitnesscenter.com or call 972.233.4832.
Article provided by Mary Edwards, MS, Cooper Fitness Center Director of Fitness and Professional Fitness Trainer.